
Alevel经济学是Alevel课程中比较重要的一门科目,提到经济就会涉及到宏观经济和微观经济概念,今天,锦秋小编要为大家介绍的是Alevel经济学中的宏观经济部分的政府干预知识点。
Fiscal Policy
1. 定义
Fiscal policy involves the manipulation of government spending, taxation and the budget balance. Fiscal policy aims to stimulate economic growth and stabilise the economy.
2. 分类
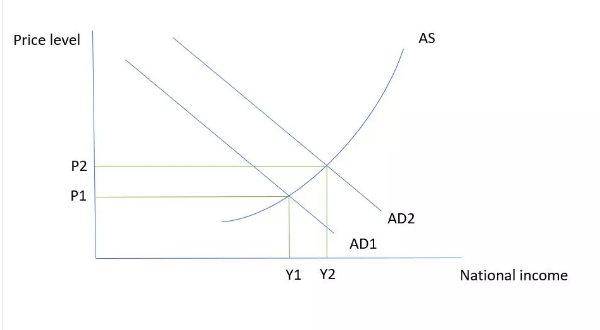
Expansionary fiscal policy
This aims to increase AD. Governments increase spending or reduce taxes to do this. It leads to a worsening of the government budget deficit, and it may mean governments have to borrow more to finance this.
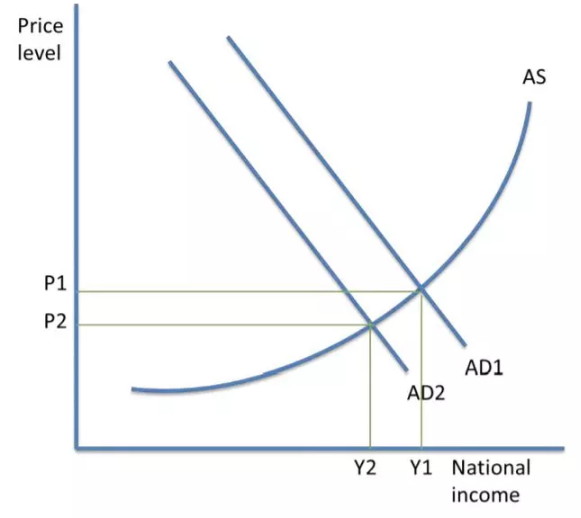
Deflationary fiscal policy
This aims to decrease AD. Governments cut spending or raise taxes, which reduces consumer spending. It leads to an improvement of the government budget deficit.
3. How fiscal policy can be used to influence AS
•The government could reduce income and corporation tax to encourage spending and investment.
•The government could subsidise training or spend more on education. This lowers costs for firms, since they will have to train fewer workers. Spending more on healthcare helps improve the quality of the labour force, and contributes towards higher productivity.
•Governments could spend more on infrastructure, such as improving roads and schools.
4. Limitations of fiscal policy
•Governments might have imperfect information about the economy. It could lead to inefficient spending.
•There is a significant time lag involved with employing fiscal policy. It could take months or years to have an effect.
•If the government borrows from the private sector, there are fewer funds available for the private sector, which could lead to crowding out.
•The bigger the size of the multiplier, the bigger the effect on AD and the more effective the policy.
•If interest rates are high, fiscal policy might not be effective for increasing demand.
•If the government spends too much, there could be difficulties paying back the debt, which could make it difficult to borrow in the future
Supply Side Policies
Supply-side policies aim to improve the long run productive potential of the economy. The economy can experience supply-side improvements in the private sector, without government intervention. For example, there could be improvements in productivity, innovation and investment.
1. Free market supply-side policies
•To increase incentives
Reducing income and corporation tax to encourage spending and investment. This could increase the long run productive potential of the economy, especially if labour and capital becomes more productive. This improves the underlying trend of economic growth.
•To promote competition
By deregulating or privatising the public sector, firms can compete in a competitive market, which should also help improve economic efficiency.
•To reform the labour market
Reducing the NMW (or abolishing it altogether) will allow free market forces to allocate wages and the labour market should clears. Reducing trade union power makes employing workers less restrictive and it increases the mobility of labour. This makes the labour market more efficient.
2. Interventionist supply-side policies
•To promote competition
A stricter government competition policy could help reduce the monopoly power of some firms and ensure smaller firms can compete, too.
•To reform the labour market
Governments could try and improve the geographical mobility of labour by subsidising the relocation of workers and improving the availability of job vacancy information.
•To improve skills and quality of the labour force
The government could subsidise training or spend more on education. This also lowers costs for firms, since they will have to train fewer workers.
Spending more on healthcare helps improve the quality of the labour force, and contributes towards higher productivity.
•To improve infrastructure
Governments could spend more on infrastructure, such as improving roads and schools.
3. Features of supply-side polices
•Supply-side policies are the only policies which can deal with structural unemployment, because the labour market can be directly improved with education and training.
•Demand-side policies are better at dealing with cyclical unemployment, since they can reduce the size of a negative output gap and shift the AD curve to the right.
•There are significant time lags associated with supply-side policies.
•Market-based supply-side policies, such as reducing the rate of tax, could lead to a more unequal distribution of wealth.
今天的分享到这里就结束了,学习经济的小伙伴们不要错过哦~如果还想了解更多关于A-level学科、考试等相关资讯信息,请扫码关注锦秋A-level,锦秋A-Level项目针对不同学员的不同层次的学习需求,设置一站式计划、G5学霸计划和国际班互补计划三大课程体系,并且有针对性的制定课程计划和教学方式,开设的课程有数学、进阶数学、物理、化学、生物、经济学、会计学等,紧抓中国学生理科优势,进行课程组合化。

| 大学名称 | QS排名 |
|---|